Mandi System In India
Mandi system in india. It is operated as per the regulations of APMC. This is actually a win-win situation if it works well. There are no taxes levied and hence the mandi fee is out if sold outside.
So this mandi system has just made the middle men in villages and small towns richer. The committee set up in 2017 by the government had recommended that India should have at least 10130 mandis. The number of mandis was to increase to at least 41000 but there were only 6630 mandis in 2019 with an average area served of 463 sqkm.
APMC regulates and manages the agricultural market. Farm laws will reform toxic mandi system but government needs to tackle misinformation. How farmers view the existing Mandi system Presently Indias agricultural markets are regulated by the states under the Agricultural Produce Marketing Committee APMC Act.
India is known for commodity forward and futures markets that existed for centuries though standardised regulated futures trading has a history of over a century only. In such a context systematic comprehensive and contextual studies across agroecological regions administrative units commodities and. Government and Farmers are at the giving end.
Gostaríamos de exibir a descriçãoaqui mas o site que você está não nos permite. Mandi system in India. But sometimes some misconceptions are created.
These traders indulge in hoarding of food items thus reducing their supply. An Agricultural Produce Market Committee APMC is a marketing board established by state governments in India to ensure farmers are safeguarded from exploitation by large retailers as well as ensuring the farm to retail price spread does not reach excessively high levels. It is not as though everything is hunky-dory with Indias current mandi system for marketing of agricultural produce by farmers.
The new farm laws seek to change the way marketing can be done. Research by Isha MalaviyaPresented Edited by Sumit Krishna YadavAs opposed to a traditional mandi system e-mandis specifically abolish the culture of midd.
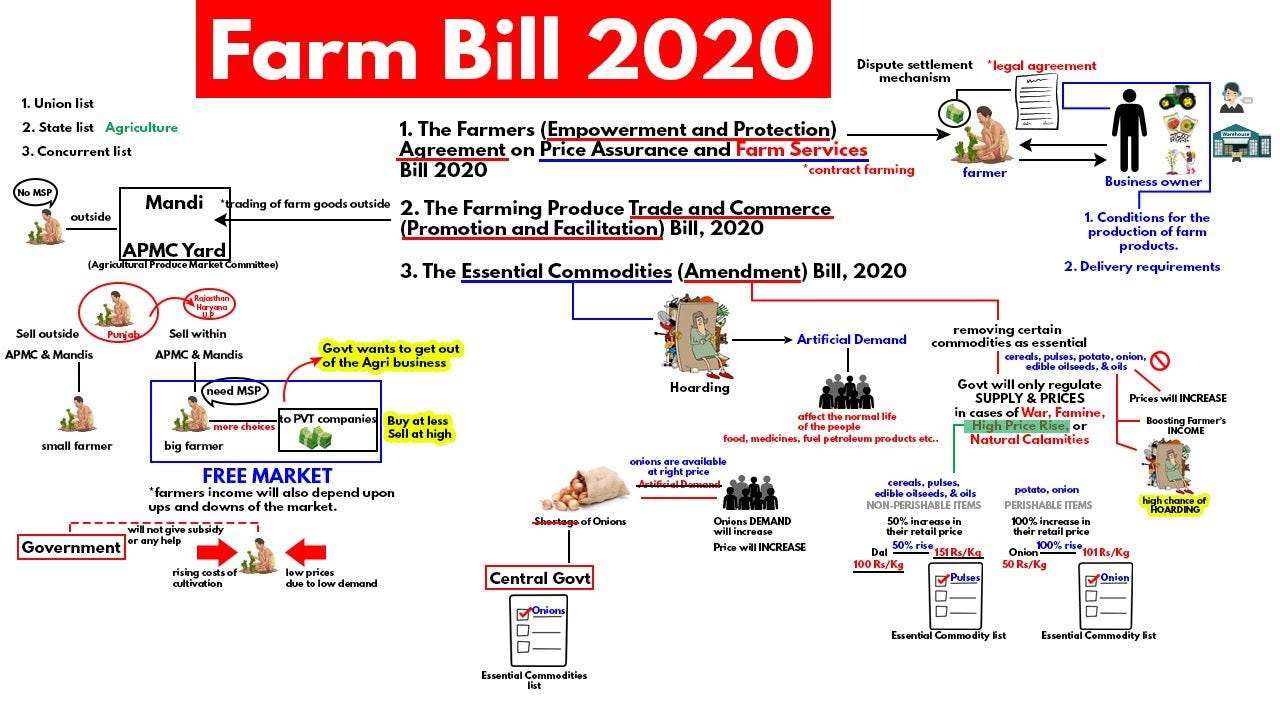
Since August 2020 the farmers of India are protesting against three new Agriculture bills now acts passed by the Parliamentone of the reasons stated is the potential of the new legislation affecting the Agricultural Produce Market Committee APMCs Mandi system.
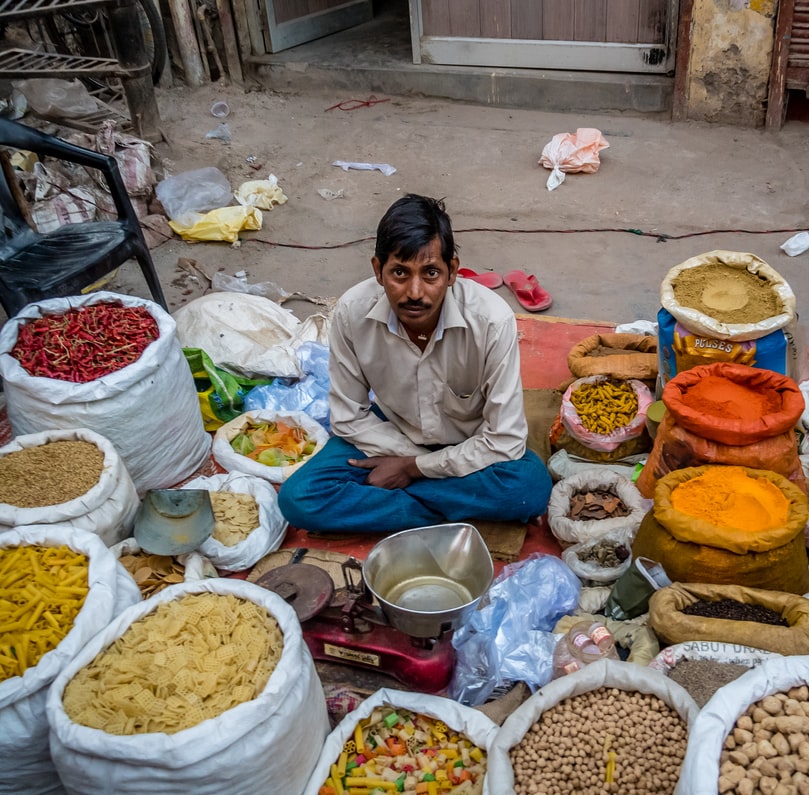
But the system helped to create a class of absentee landlords who were more interested in squeezing higher land rents than in real agricultural progress. Surjewala says ending MSP and mandi system is governments move. Mandis or physical primary agricultural markets are old and ubiquitous institutions of economic life in many parts of India. The mandi is basically a market place where farmers sell their produce to the buyers through AUCTION. APMC regulates and manages the agricultural market. In Punjab and Haryana the mandi system is strong so a perception was created that APMCs will now be finished The minister also said that the tax collected from government APMCs will benefit farmers in the long run. Zamindari system the British were able to create a class of people whose interests were directly tied to British rule in India. Like Indias agricultural markets our information about them is also highly fragmented and our data disorganised intermediated and incomplete. The quote is understandable and to an extent even sublime.
Unregulated futures markets are often called Satta Bazar. Mandis or physical primary agricultural markets are old and ubiquitous institutions of economic life in many parts of India. The second bill gives freedom to enter into agreements with the firms that buy crops. The new farm laws seek to change the way marketing can be done. India is known for commodity forward and futures markets that existed for centuries though standardised regulated futures trading has a history of over a century only. There are no taxes levied and hence the mandi fee is out if sold outside. APMCs are regulated by states through their adoption of a Agriculture Produce Marketing Regulation APMR Act.














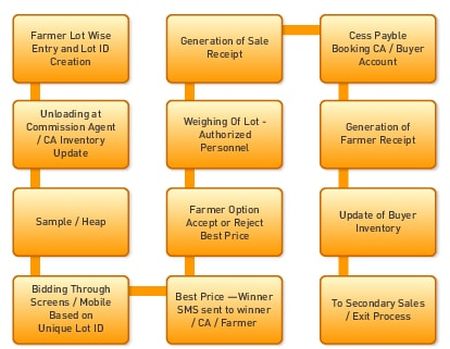
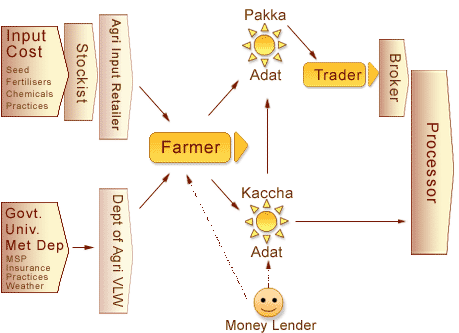




















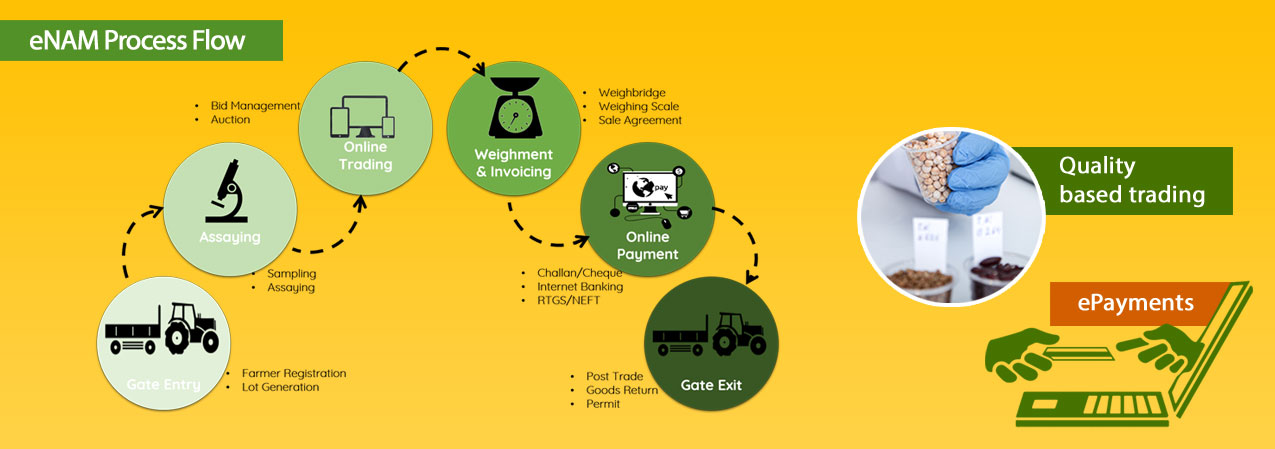





Post a Comment for "Mandi System In India"